
News
Accessible Instruction
Advocating for Education Inclusive of Deaf Individuals in Nepal
January 2, 2024
Translated from Nepali Sign Language.
KATHMANDU, Nepal – Nepal has between 250,000 and one million Deaf people, but most do not attend school. In many schools for Deaf individuals, education ends at 10th grade, and higher education is rarely available and often inadequate.
Satya Devi Wagle is a renowned Deaf rights advocate in Nepal, known for her unwavering dedication to inclusion. She serves as the vice president of the National Federation of the Deaf Nepal (NDFN) and the president of the Kathmandu Association of the Deaf. Through her initiatives, she has successfully reduced communication barriers and paved the way for better employment and education opportunities for Deaf individuals. Her efforts focus on fostering an inclusive atmosphere where every individual’s voice is heard and potential realized.
DJP Fellow Bishwamitra Bhitrakoti interviews Wagle about the strategies, challenges and successes of her work on inclusive education for Deaf individuals.
Question: What are some of the biggest problems with inclusive Deaf education in Nepal?
Answer: There isn’t enough infrastructure, qualified teachers or educational supplies to enable inclusive education for Deaf students in Nepal. Hearing students need oral methods and Deaf students need sign language to study together. Until now, the infrastructure and human resources to achieve this haven’t been developed.
Question: Can you describe your organization’s approach to achieving your vision for inclusive education for Deaf people in Nepal?
Answer: We at NDFN are lobbying for high-quality education for children with hearing disabilities in Nepal with the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, as well as the Centre for Education and Human Resource Development (CEHRD). We are in discussions with the Curriculum Development Centre (CDC) and CEHRD on how we can create a Deaf-friendly curriculum.
Question: What do you expect from the Nepal government in this regard?
Answer: The government’s national policies, such as the education policy, should include a program and budget for Deaf education. Enough budget should be allocated for the schools where children with disabilities study. We don’t see that provision. But, we can see there is a huge budget allocated by the government to mainstream schools. [Once] when we translated 60 school lessons chosen from different disciplines into the Nepali Sign Language, we saw very effective results in the learning outcomes of children with hearing disabilities.
Question: What specific initiatives or technologies for access to communication has your organization sponsored for Deaf people in Nepali educational institutions?
Answer: NDFN launched the MERO SIKAI and MERO SANKET mobile apps for Deaf children [to support] their learning. (MERO SIKAI is an inclusive app with Nepali Sign Language accessibility that supports children in improving their reading skills. MERO SANKET is an app that teaches Nepali Sign Language.) We are encouraging the use of these two apps to Deaf schools along with TVs, monitors, and smartboards instead of whiteboards. It would be very beneficial for children with hearing disabilities to use new technology.
Question: Does your organization promote awareness of Deaf culture and the needs of the Deaf community among the general public?
Answer: The hearing community in Nepal is unaware of the Deaf community and their needs. There are a lot of Deaf people who are uneducated. Many elderly Deaf people never got an education. NDFN advocates with the stakeholders of 53 affiliated district Deaf associations. The districts are raising awareness about Deaf culture in their regions. We also organize awareness programs on TV occasionally.
Question: To encourage inclusion and facilitate integration, what alliances or partnerships have you established with mainstream educational institutions? How do you work with them?
Answer: Because hearing teachers are not competent in sign language, there is no quality instruction in a resource class in Nepal. We (NDFN) are working with the CEHRD (Centre for Education and Human Resource Development) to create a Deaf-friendly curriculum. Sign language instruction tools for Deaf pupils are scarce. We need to work on it, and we are also developing some instructional materials with support from the donor. Open communication, a common vision, and a commitment to establishing an inclusive and supportive educational environment for all students are required for successful partnerships.
Question: Could you tell us about your future plans with respect to inclusive Deaf education in Nepal?
Answer: Our future plans include establishing a good structure, developing human resources, researching and developing a new sign language and establishing a training center. We also want to develop a close relationship with the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, and the Centre for Education and Human Resource Development. We can’t do it all by ourselves. We need to collaborate with the Nepal government and other stakeholders for inclusive education.
Bishwamitra Bhitrakoti is a Deaf youth from Annapurna Rural Municipality, Kaski, Nepal. Born into a Dalit community, he has challenged casteism as part of his advocacy work. As a communications officer at the National Federation of the Deaf, Nepal, Bhitrakoti focuses on strategic communication planning, fostering media relations, and creating universally designed content.
News From the Global Frontlines of Disability Justice
Rwanda’s Marburg Crisis
As Rwanda confronts its first-ever Marburg virus outbreak, people with disabilities face heightened risks — not only from the virus but also from the lack of accessible health information. “Without proper accommodations, such as sign language interpreters, captions, Braille, or visual aids, the Deaf and DeafBlind community may miss crucial information about how to protect themselves, symptoms to watch for, or where to seek help in case of infection,” says Joseph Musabyimana, executive director of the Rwanda Organization of Persons with Deaf Blindness.
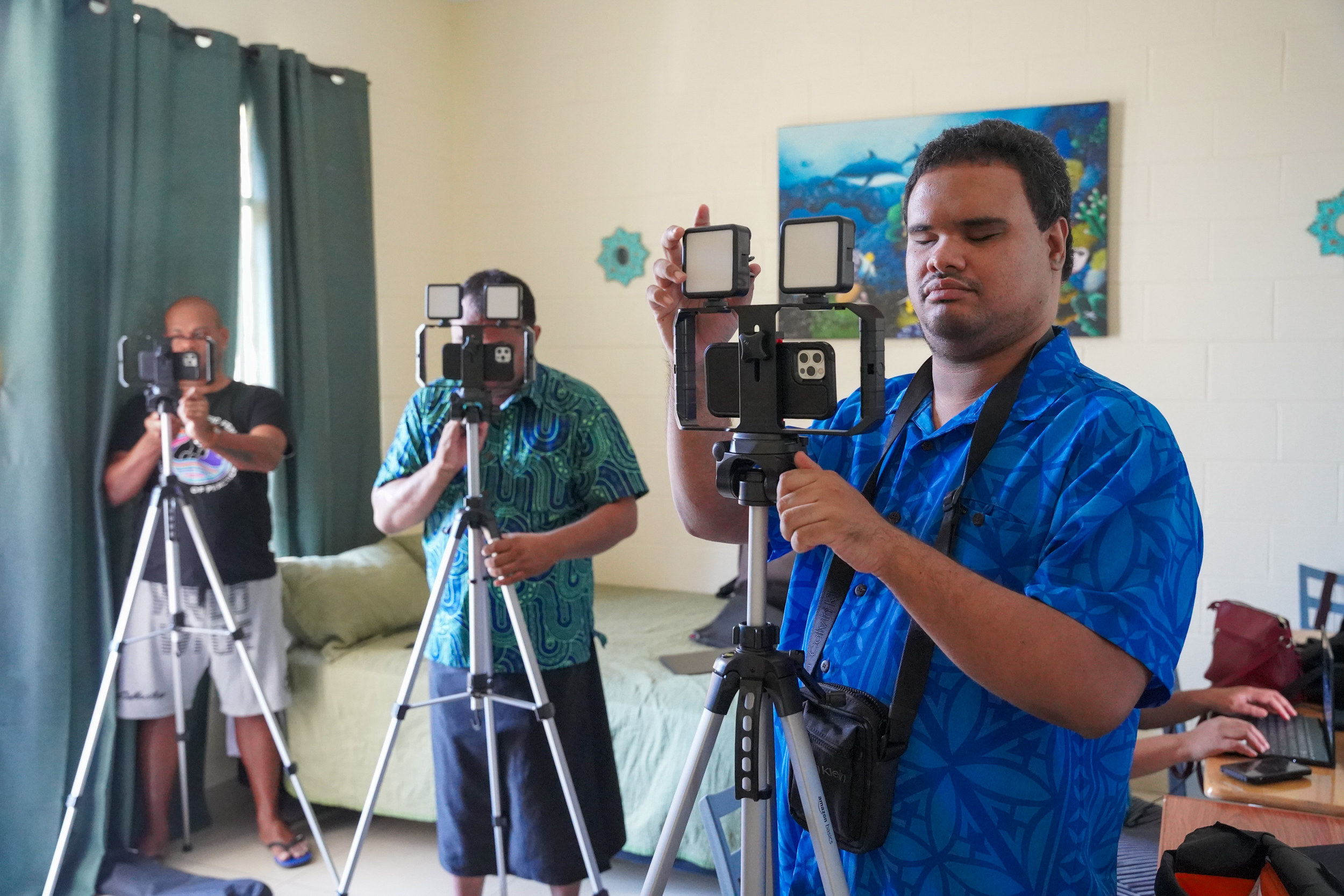

Capturing Vision Through Sound and Touch
Last summer, the DJP trained Indigenous activists with disabilities from the Pacific on the iPhone camera to create a documentary series on disability and climate change. With VoiceOver, the iPhone provides image descriptions for blind and low-vision filmmakers and offers other accessible features. “If you think about it, it doesn’t make sense for a blind person to use a camera,” says DJP filmmaker Ari Hazelman. “The iPhone gives you more avenues to tell your story in a more profound way as a blind person.”

Work for All
The We Can Work program equips young Rwandans with disabilities to navigate barriers to employment through education, vocational training, and soft skills development. By fostering inclusive workplaces and advocating for policy changes, the program aims to reduce poverty and promote economic independence. Participants like Alliance Ukwishaka are optimistic that the program will enable them to achieve their dreams and showcase their potential. The initiative is part of a larger effort to support 30 million disabled youth across seven African countries.

Global Recognition
Faaolo Utumapu-Utailesolo’s film “Dramatic Waves of Change” has been named a finalist in the Focus on Ability International Short Film Festival. The film, completed during a Disability Justice Project workshop in Samoa, highlights the impact of climate change on people with disabilities in Kiribati. Utumapu-Utailesolo, who is blind, used an iPhone with accessibility features to create the film. “Do not leave people with disabilities behind when [you] plan, implement, and monitor programs regarding climate change and disaster,” she says. Her achievement is a testament to the power of inclusive filmmaking.
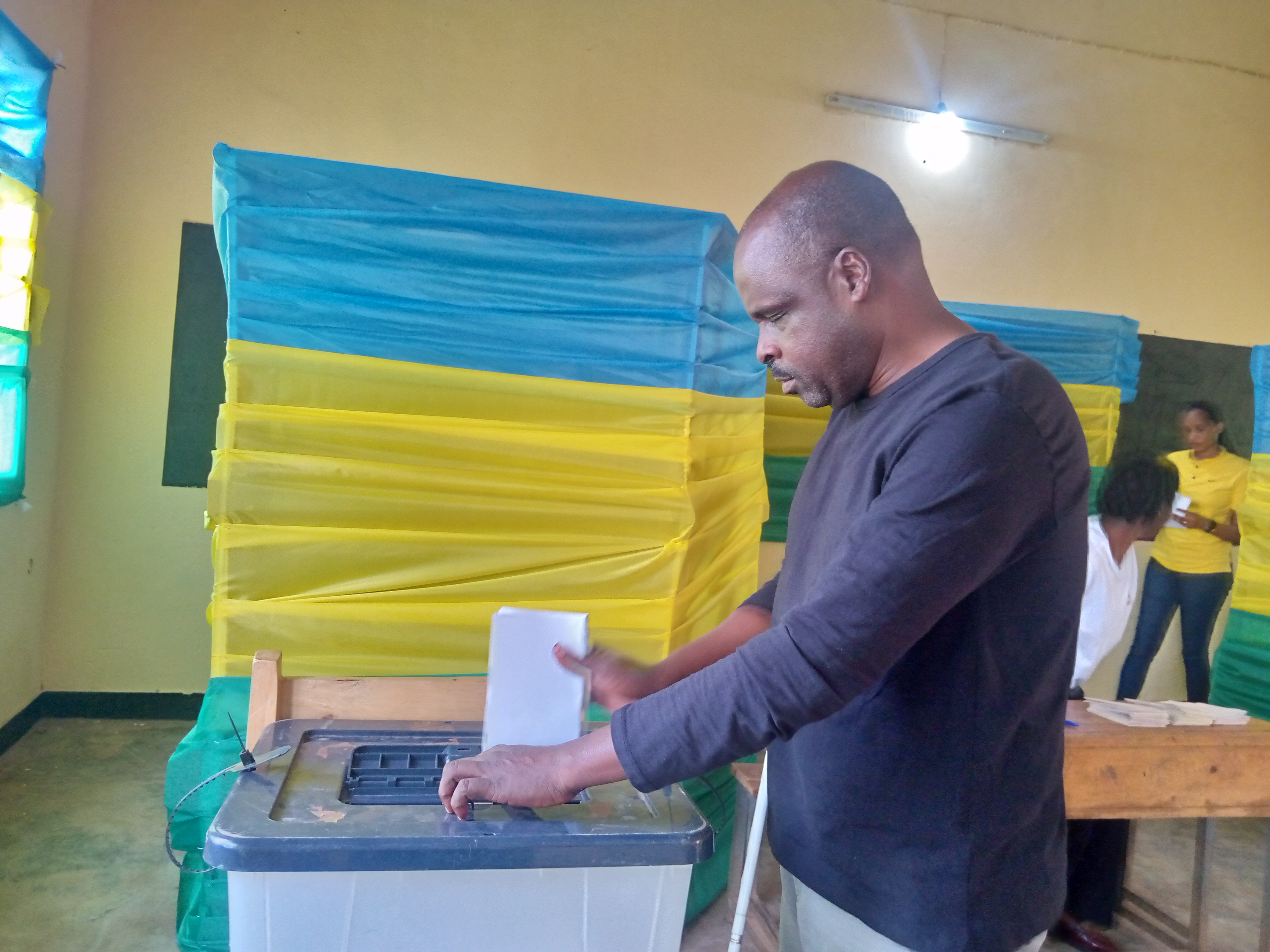

Advancing Democracy
Rwanda has made significant progress in making its elections more accessible, highlighted by the July 15 general elections where notable accommodations were provided. This was a major step forward in disabled Rwandans’ quest for equal rights and participation. “You cannot imagine how happy I am, for I have voted by myself and privately as others do accessibly,” says Jean Marie Vianney Mukeshimana, who used a Braille voting slate for the first time. “Voting is a deeply emotional and meaningful experience for a person with any disability in Rwanda, reflecting a blend of pride, empowerment, and hope.”
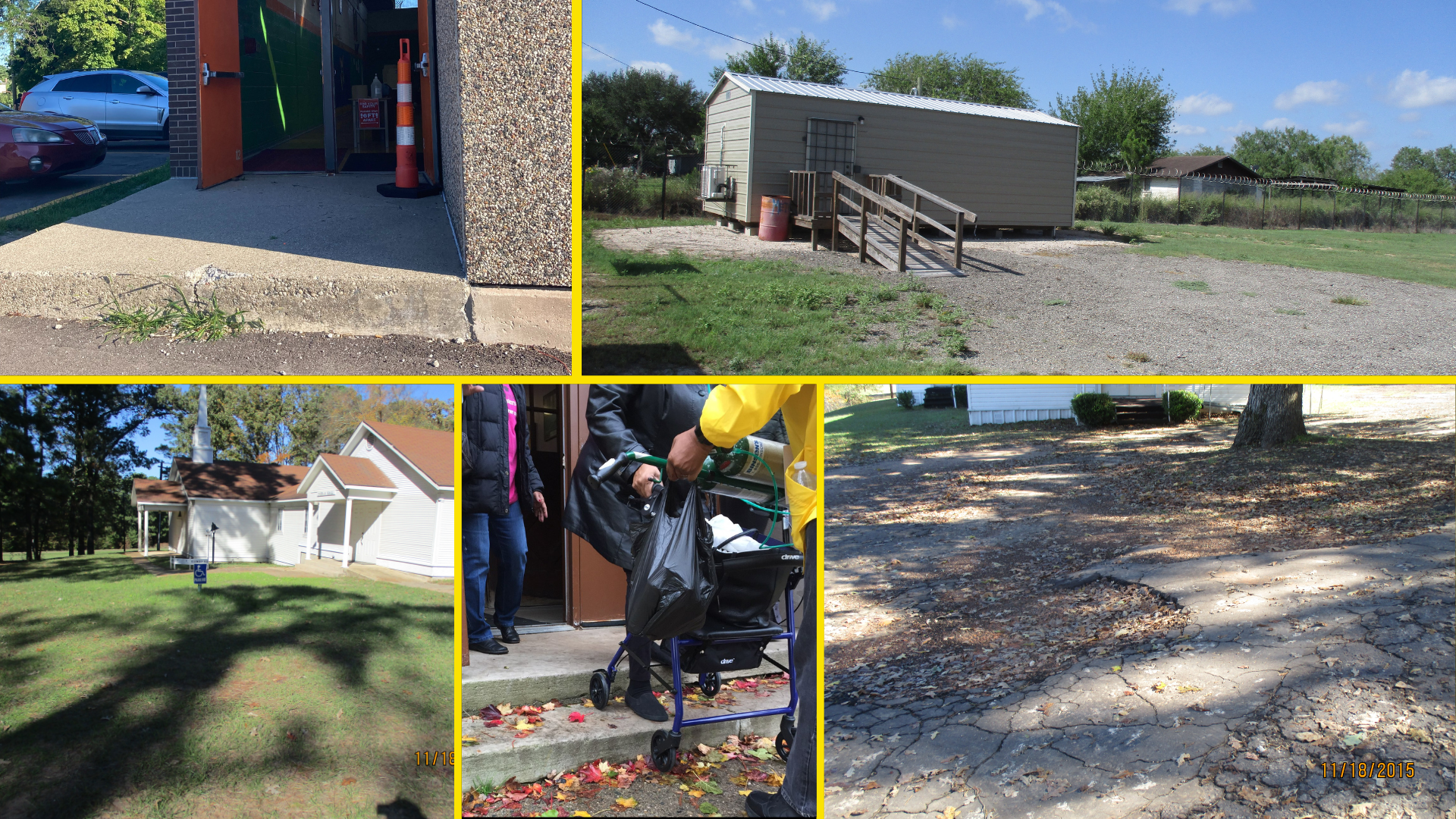

Barriers to the Ballot
Despite legislation like the Americans with Disabilities Act, barriers at the polls still hinder — and often prevent — people with disabilities from voting. New restrictive laws in some states, such as criminalizing assistance with voting, exacerbate these issues. Advocacy groups continue to fight for improved accessibility and increased voter turnout among disabled individuals, emphasizing the need for multiple voting options to accommodate diverse needs. ““Of course, we want to vote,” says Claire Stanley with the American Council of the Blind, “but if you can’t, you can’t.”