
News
‘Count Me In, In Any Change You Make’
DJP Fellow Melvina Voua Advocates For the Full Inclusion of Solomon Islanders with Disabilities in Government Responses to Climate Change
July 1, 2023
APIA, Samoa – DJP Fellow Melvina Voua, from the Solomon Islands, works for People with Disability Solomon Island (PWDSI) as a climate change officer. She is advocating for the full inclusion of persons with disabilities in all aspects of climate change adaptation and mitigation.
Question: Can you share your experience of your journey of being a climate change advocate for persons with disabilities?
Answer: I started working with PDF [Pacific Disability Forum] in 2020 as a part-time climate change officer. I was the focal point person for the Solomon Islands in the climate change research conducted for the three countries of Solomon Islands, Kiribati and Tuvalu to coordinate the research on the impact of climate change on people living with disability in the Solomon Islands.
Question: What are the challenges that you faced in implementing this work?
Answer: The big challenge is the COVID, in 2019, 2020 and 2021 while we were doing the research. So all of the learnings and findings we had to do activities online with the PDF, such as when we trained our response team and training team to collect information from other persons with disabilities and their stories, so it’s kind of challenging to get stories like how were they impacted by climate change, how do they prepare for the disaster.
Question: What is the challenge you face in working with key stakeholders?
Answer: It’s a big challenge. Also, it’s a bit difficult to approach them, so when we try to engage them or approach them for our consultation, they all, like, have other commitments. So we can’t really get what information we want from them. So yeah, that’s the big challenge for me.
Question: What is your message to the government?
Answer: It is very important for the inclusion of persons with disability in all the plans or starting from a grassroots level up to the national level. All the adaptation and mitigation plans must be inclusive and not excluding people with disability, like when designing evacuation centers or developing policies for climate change or disasters. It should make sure that disability must be included in the planning because when the crisis or the disaster happen, we always find it difficult to evacuate or access or even get prepared or respond. So that’s why it’s very important to include the needs of persons with disability in preparedness activities or programs.
DJP Fellow Sa Utailesolo has been working at the National Advocacy Organisation of Persons with Disabilities, Nuanua O Le Alofa (NOLA), in Samoa as a finance and administration coordinator for nearly 15 years. In the past, he has also worked as a Braille translator. @2023 NOLA. All rights reserved.
News From the Global Frontlines of Disability Justice
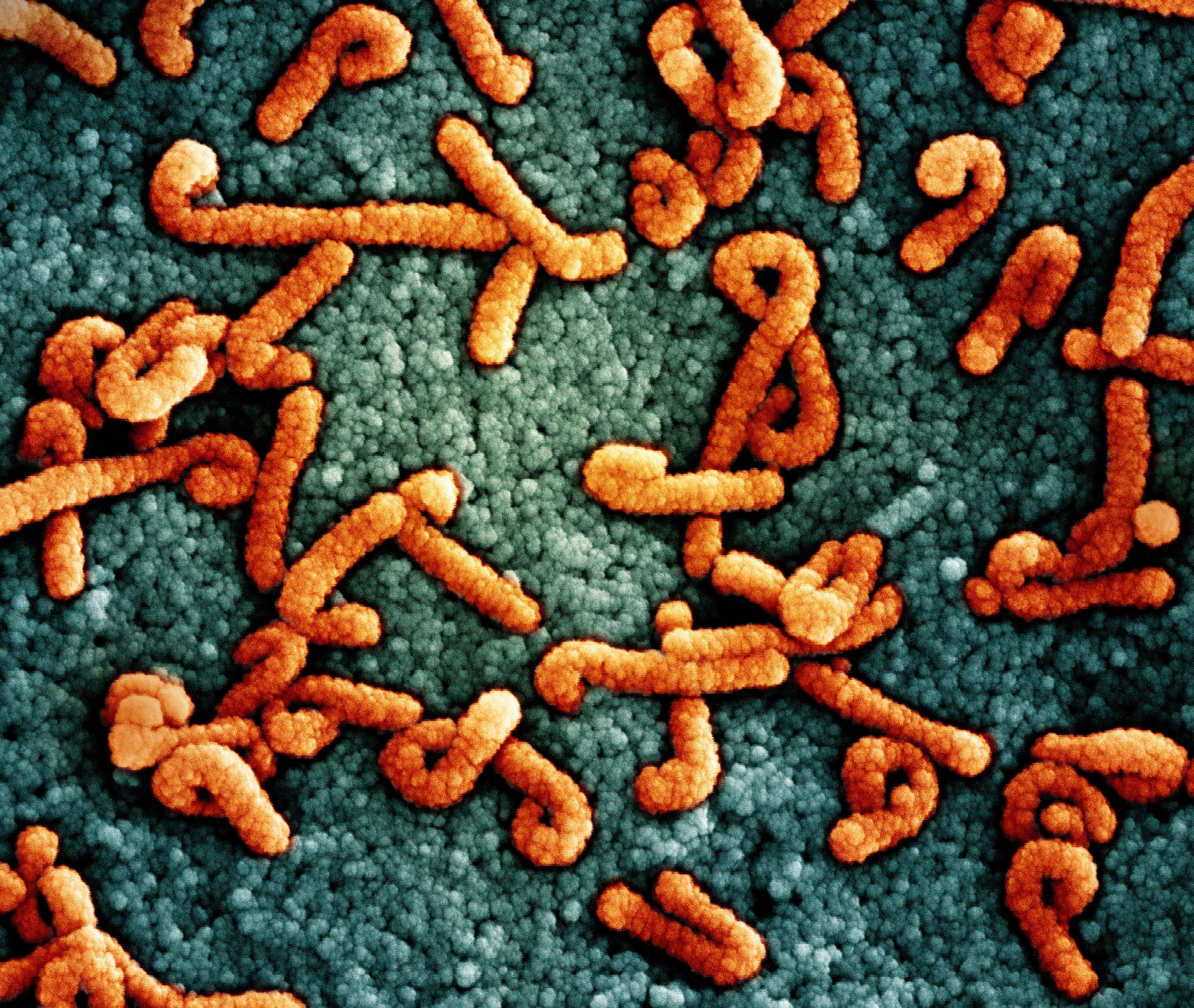
Rwanda’s Marburg Crisis
As Rwanda confronts its first-ever Marburg virus outbreak, people with disabilities face heightened risks — not only from the virus but also from the lack of accessible health information. “Without proper accommodations, such as sign language interpreters, captions, Braille, or visual aids, the Deaf and DeafBlind community may miss crucial information about how to protect themselves, symptoms to watch for, or where to seek help in case of infection,” says Joseph Musabyimana, executive director of the Rwanda Organization of Persons with Deaf Blindness.
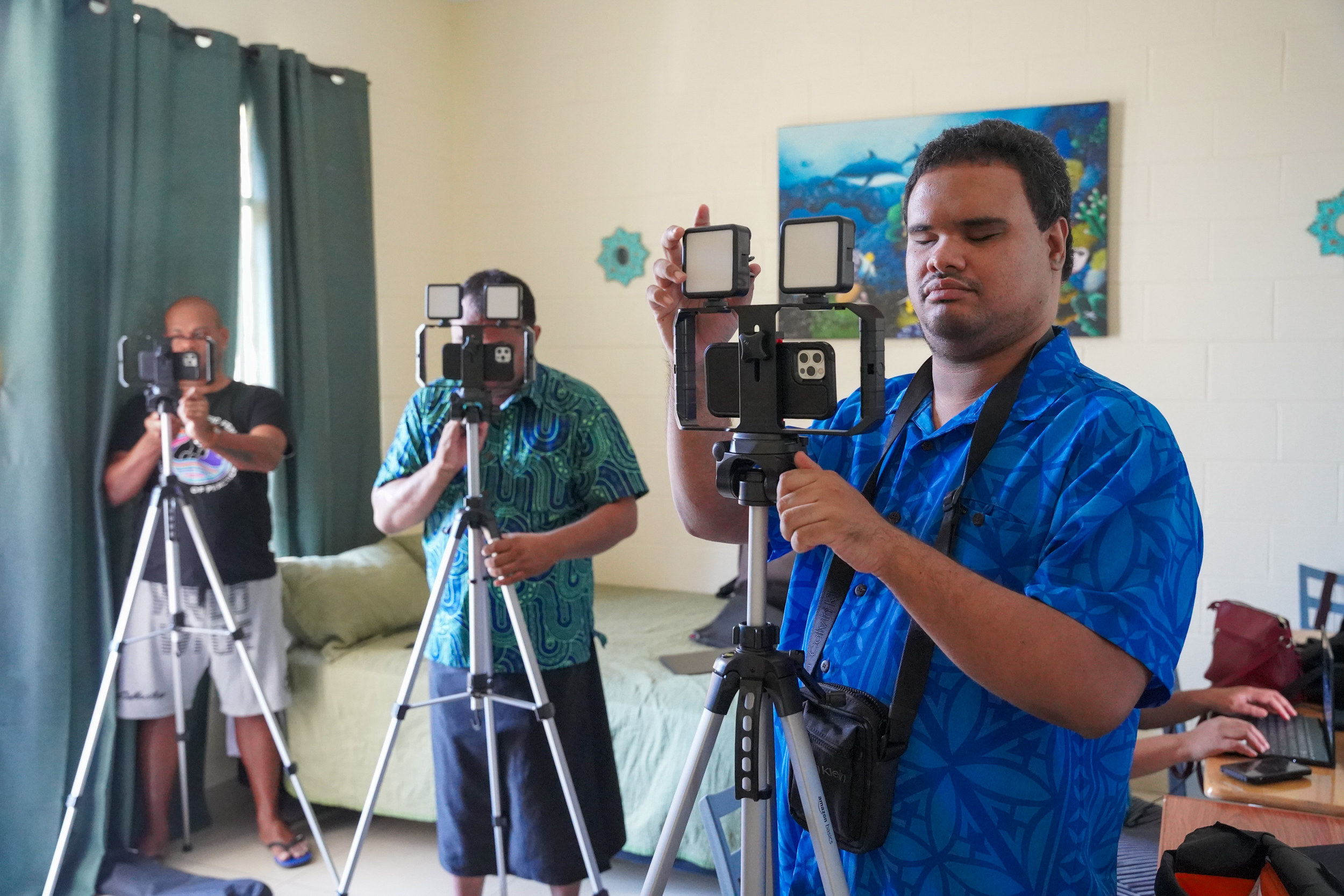

Capturing Vision Through Sound and Touch
Last summer, the DJP trained Indigenous activists with disabilities from the Pacific on the iPhone camera to create a documentary series on disability and climate change. With VoiceOver, the iPhone provides image descriptions for blind and low-vision filmmakers and offers other accessible features. “If you think about it, it doesn’t make sense for a blind person to use a camera,” says DJP filmmaker Ari Hazelman. “The iPhone gives you more avenues to tell your story in a more profound way as a blind person.”

Work for All
The We Can Work program equips young Rwandans with disabilities to navigate barriers to employment through education, vocational training, and soft skills development. By fostering inclusive workplaces and advocating for policy changes, the program aims to reduce poverty and promote economic independence. Participants like Alliance Ukwishaka are optimistic that the program will enable them to achieve their dreams and showcase their potential. The initiative is part of a larger effort to support 30 million disabled youth across seven African countries.

Global Recognition
Faaolo Utumapu-Utailesolo’s film “Dramatic Waves of Change” has been named a finalist in the Focus on Ability International Short Film Festival. The film, completed during a Disability Justice Project workshop in Samoa, highlights the impact of climate change on people with disabilities in Kiribati. Utumapu-Utailesolo, who is blind, used an iPhone with accessibility features to create the film. “Do not leave people with disabilities behind when [you] plan, implement, and monitor programs regarding climate change and disaster,” she says. Her achievement is a testament to the power of inclusive filmmaking.
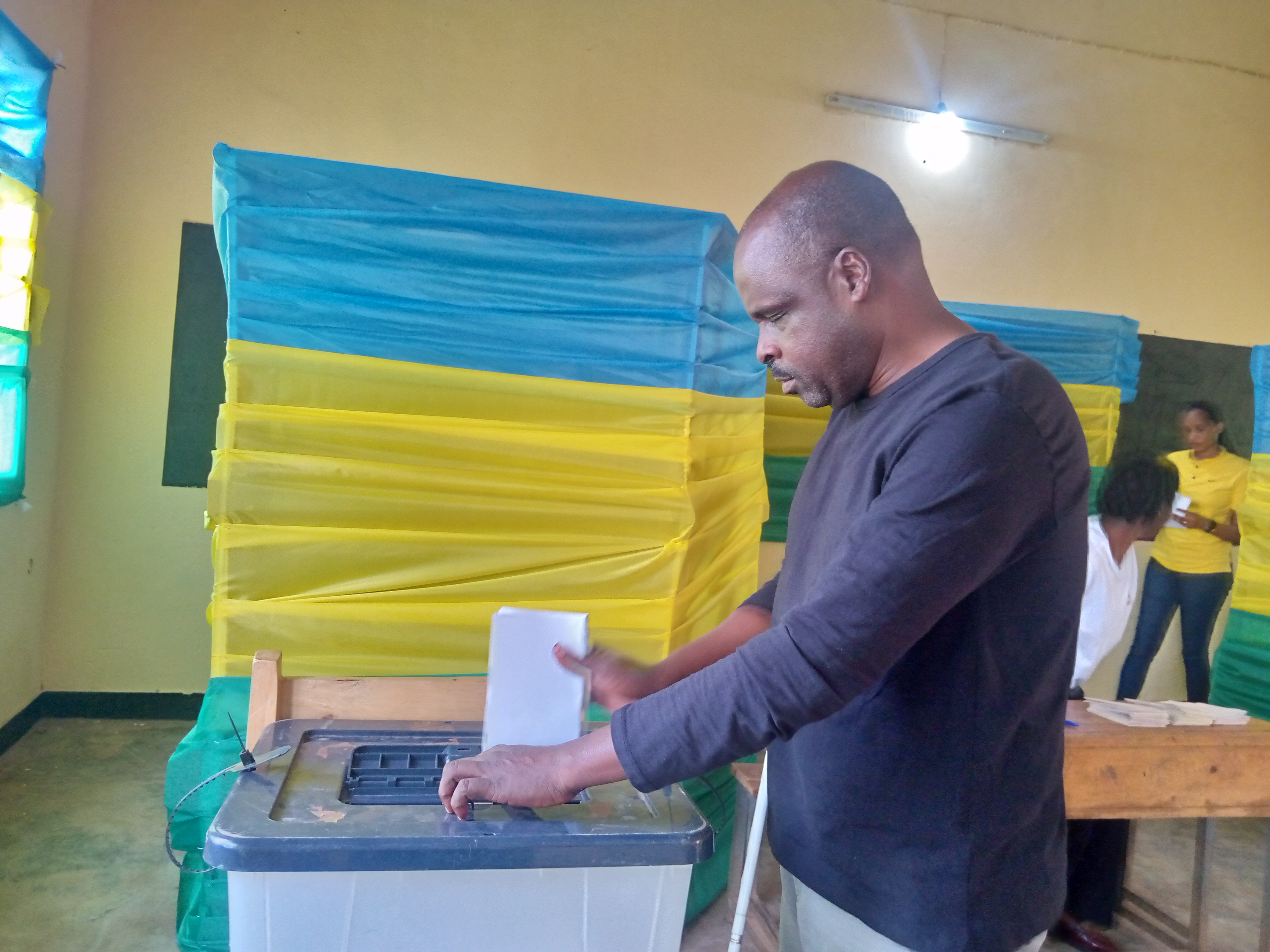

Advancing Democracy
Rwanda has made significant progress in making its elections more accessible, highlighted by the July 15 general elections where notable accommodations were provided. This was a major step forward in disabled Rwandans’ quest for equal rights and participation. “You cannot imagine how happy I am, for I have voted by myself and privately as others do accessibly,” says Jean Marie Vianney Mukeshimana, who used a Braille voting slate for the first time. “Voting is a deeply emotional and meaningful experience for a person with any disability in Rwanda, reflecting a blend of pride, empowerment, and hope.”
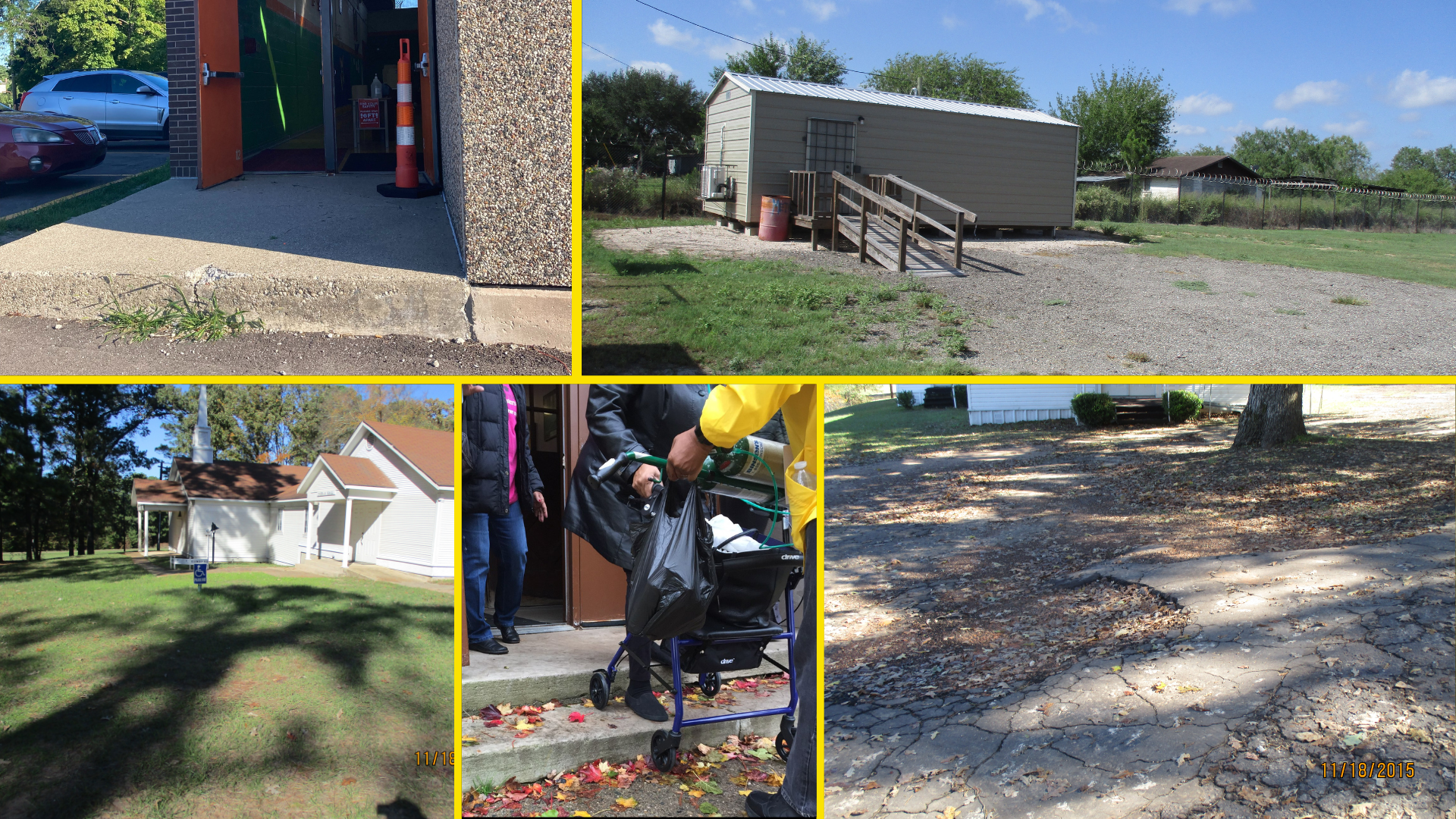

Barriers to the Ballot
Despite legislation like the Americans with Disabilities Act, barriers at the polls still hinder — and often prevent — people with disabilities from voting. New restrictive laws in some states, such as criminalizing assistance with voting, exacerbate these issues. Advocacy groups continue to fight for improved accessibility and increased voter turnout among disabled individuals, emphasizing the need for multiple voting options to accommodate diverse needs. ““Of course, we want to vote,” says Claire Stanley with the American Council of the Blind, “but if you can’t, you can’t.”