
News
Leaving No One Behind
Play audio version
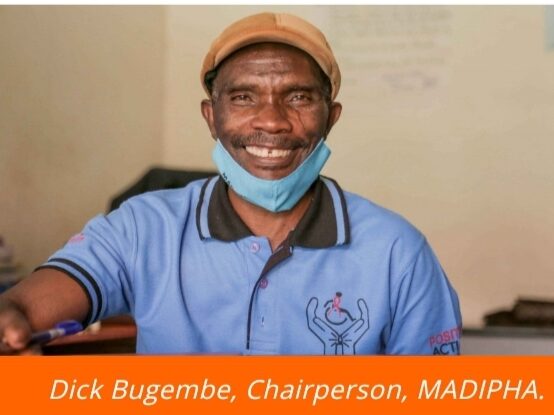
Dick Bugembe Fights for Equal Access to HIV/AIDS Services and Information
November 4, 2021
MASAKA, Uganda — Fifty-eight years ago, Dick Bugembe was born with a symbrachydactyly, a rare congenital condition in which a person has short fingers that may be webbed or joined. Because of damage to his nervous system, his gait was also unsteady. As a young child with a disability, Bugembe wasn’t afraid to pursue his dreams, and he grew up to become a politician in Uganda and also the founding member of the Masaka Association of Disabled Persons Living with HIV & AIDS (MADIPHA).
When Bugembe was first diagnosed with HIV/AIDS in 2009, he thought of it as a death sentence. “I lost hope because I thought I was the only one with HIV and at the same time living with a disability,” he says. “I thought I was about to die and perish very soon.” Like others in his village, Bugembe had the misconception that people with disabilities couldn’t get infected with HIV. He was deeply affected after taking several tests and finding out that he was indeed HIV positive. He could not imagine going through the rest of his life swallowing antiretroviral drugs and undergoing antiretroviral therapy. “I met a number of doctors and therapists who gave me different counseling sessions and real-life lessons that helped me retrieve my sense of knowledge and understanding of life living with HIV,” he says.
HIV stands for “human immunodeficiency virus” – the virus that causes AIDS and interferes with the body’s ability to fight infections. The virus can be transmitted through contact with infected blood, semen, or virginal fluids. Bugembe explains that “at that time, people with disabilities living with HIV were not known, as a few of them were being silently stigmatized and discriminated. From the training with my counselors, I knew that time does not heal anything. It’s how we deal with that time that determines the speed at which we heal.” Bugembe obtained a job at The AIDS Support Organization (TASO), an indigenous HIV and AIDS service initiative registered in Uganda as a non-governmental organization. This is when he came up with the idea to create awareness that people with disabilities can contract HIV/AIDS and that everyone should be vigilant and take a blood test for HIV.
While at TASO, Bugembe says,” I noticed a number of people living with disabilities and HIV approaching the health centers seeking HIV services and information. Some of these patients had difficulty in walking that made it so inconveniencing to move to the health center for HIV/AIDS services and information because the infrastructures were physically inaccessible.” Bugembe also noticed a lack of sign language interpreters and a lack of communications in formats such as Braille, audio, or plain languages. This made it difficult for patients who were Deaf or blind or had intellectual disabilities to access life-saving information and services. For all of these reasons, he decided to form MADIPHA in 2009.
Since then, Bugembe has been the chairperson of MADIPHA, an association based in the Masaka District of Uganda. MADIPHA’s mission is to create a society where all people with disabilities living with HIV/AIDS have equal and timely access to adequate HIV/AIDS information and services without discrimination.
MADIPHA has worked with people with disabilities, HIV service providers, organizations of persons with disabilities (OPDs), and local leaders, specifically targeting people with disabilities affected by HIV/AIDS in the greater Masaka sub-region. MADIPHA typically delivers integrated programs using the following approaches: communicating the disability and HIV/AIDS paradox, social livelihood and economic empowerment, and human rights through advocacy and collaboration.
The UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) ratified by Uganda in September 2008 estimates that, worldwide, at least 4 out of every 25 persons have disabilities. Applying this estimate to Uganda’s population of approximately 34 million, an estimated 5.4 million people with disabilities are living in Uganda. In terms of HIV/AIDS rates, UNAIDS data estimates 1.5 million Ugandans are living with HIV, and in 2019 there were 53,000 new infections and 21,000 AIDS-related deaths. Bugembe and his counterparts from the sub-region of the Masaka District intend to continue to fight the spread of HIV among people with disabilities. “When it comes to fighting HIV/AIDS,” he says, “no one should be left behind because we are all potential victims of disability and HIV/AIDS.”
The UNAIDS 2016-2021 strategy calls for fast-tracking the worldwide HIV response and reaching those people who are being left behind. The strategy highlights the bold effort needed to reach the 90-90-90 targets, which aim to bring HIV testing and treatment to the vast majority of people living with HIV and to reduce the amount of HIV in their bodies to undetectable levels. Among other suggestions, the report says that reaching this goal will require zero discrimination, a person-centered response, and equal access to health programs and services, including sexual and reproductive health.
Nissy Namuyomba is a 2021 DJP Fellow and an administrative assistant at MADIPHA. @2021 MADIPHA. All rights reserved.
News From the Global Frontlines of Disability Justice
Rwanda’s Marburg Crisis
As Rwanda confronts its first-ever Marburg virus outbreak, people with disabilities face heightened risks — not only from the virus but also from the lack of accessible health information. “Without proper accommodations, such as sign language interpreters, captions, Braille, or visual aids, the Deaf and DeafBlind community may miss crucial information about how to protect themselves, symptoms to watch for, or where to seek help in case of infection,” says Joseph Musabyimana, executive director of the Rwanda Organization of Persons with Deaf Blindness.
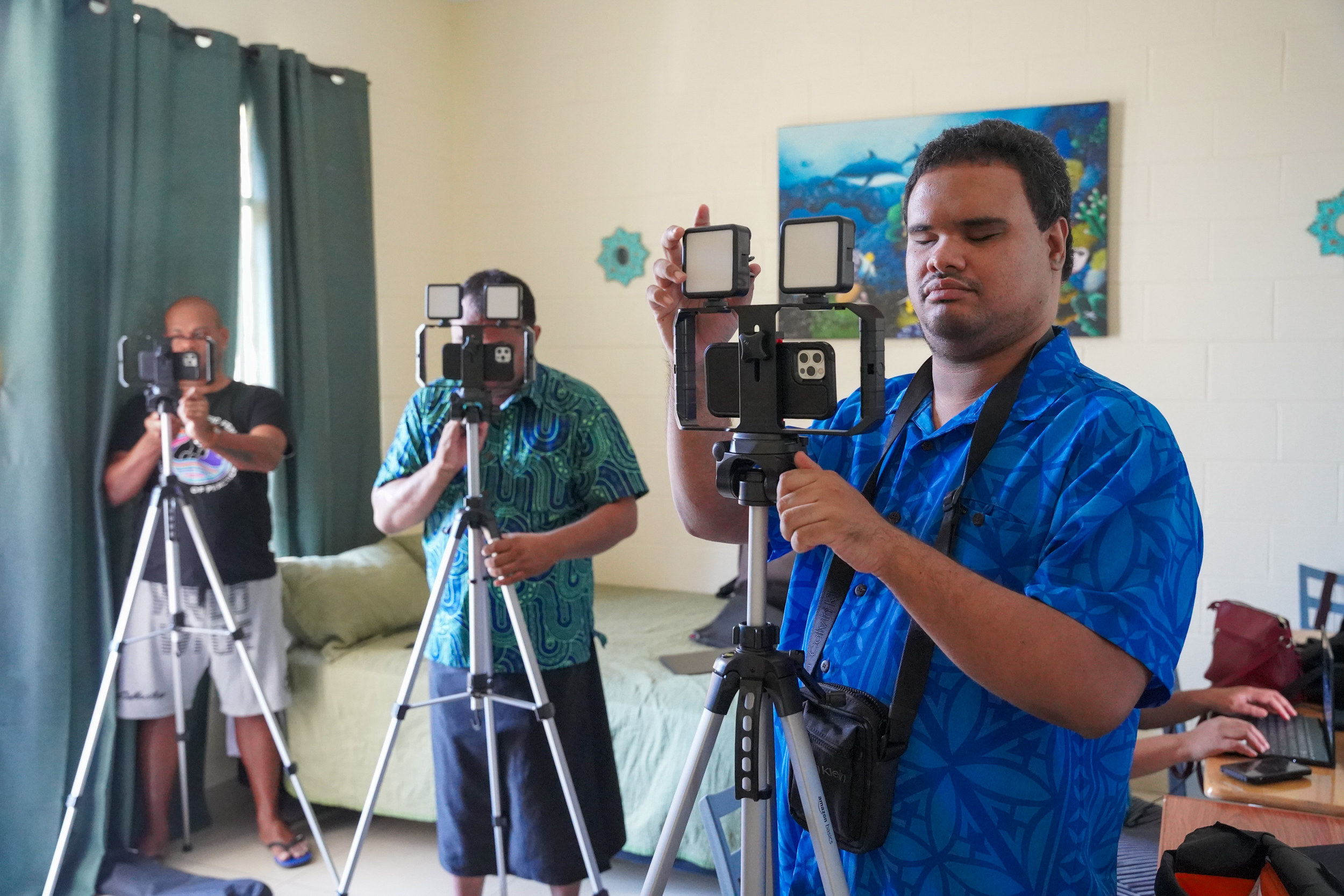

Capturing Vision Through Sound and Touch
Last summer, the DJP trained Indigenous activists with disabilities from the Pacific on the iPhone camera to create a documentary series on disability and climate change. With VoiceOver, the iPhone provides image descriptions for blind and low-vision filmmakers and offers other accessible features. “If you think about it, it doesn’t make sense for a blind person to use a camera,” says DJP filmmaker Ari Hazelman. “The iPhone gives you more avenues to tell your story in a more profound way as a blind person.”

Work for All
The We Can Work program equips young Rwandans with disabilities to navigate barriers to employment through education, vocational training, and soft skills development. By fostering inclusive workplaces and advocating for policy changes, the program aims to reduce poverty and promote economic independence. Participants like Alliance Ukwishaka are optimistic that the program will enable them to achieve their dreams and showcase their potential. The initiative is part of a larger effort to support 30 million disabled youth across seven African countries.

Global Recognition
Faaolo Utumapu-Utailesolo’s film “Dramatic Waves of Change” has been named a finalist in the Focus on Ability International Short Film Festival. The film, completed during a Disability Justice Project workshop in Samoa, highlights the impact of climate change on people with disabilities in Kiribati. Utumapu-Utailesolo, who is blind, used an iPhone with accessibility features to create the film. “Do not leave people with disabilities behind when [you] plan, implement, and monitor programs regarding climate change and disaster,” she says. Her achievement is a testament to the power of inclusive filmmaking.
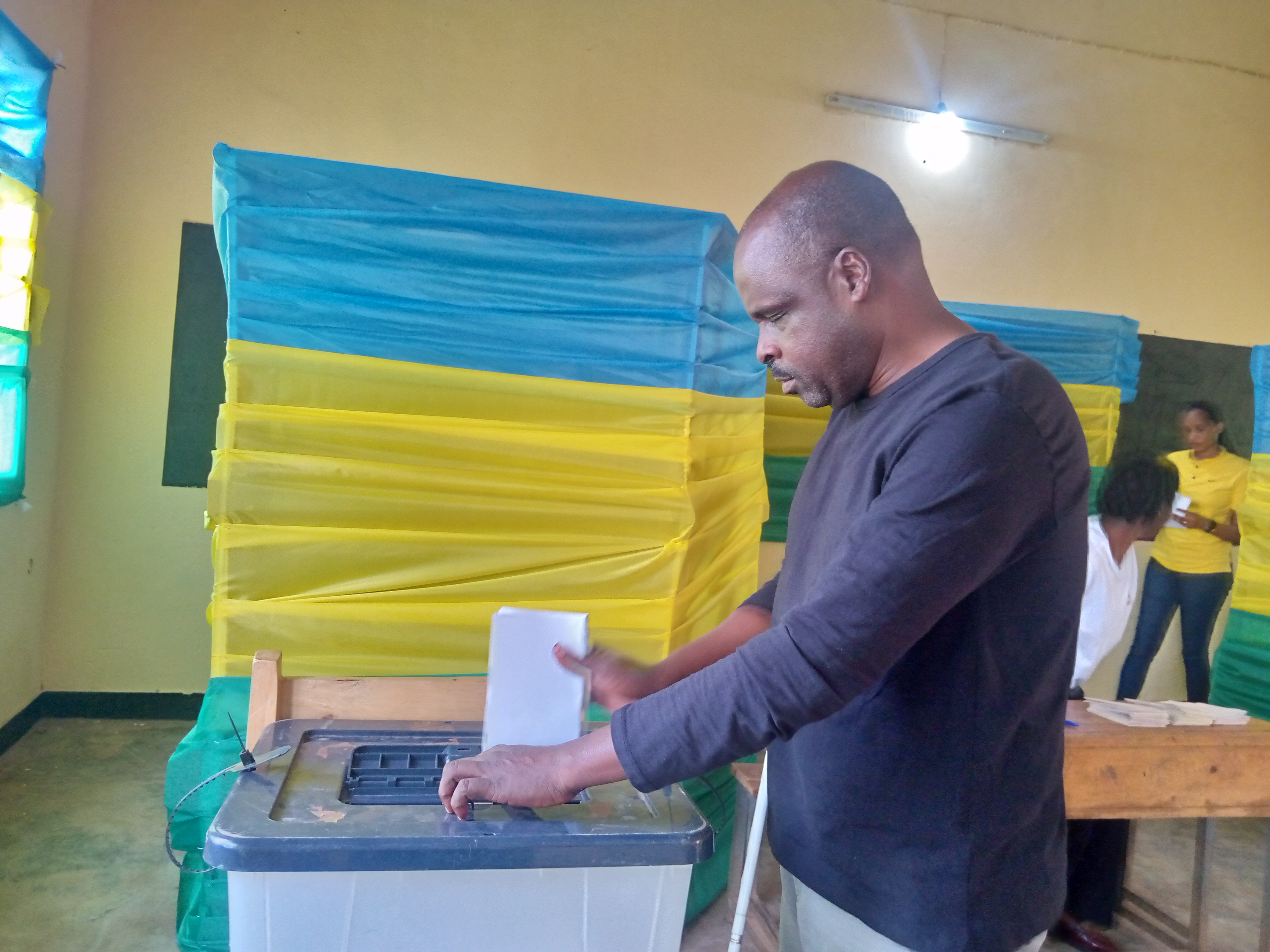

Advancing Democracy
Rwanda has made significant progress in making its elections more accessible, highlighted by the July 15 general elections where notable accommodations were provided. This was a major step forward in disabled Rwandans’ quest for equal rights and participation. “You cannot imagine how happy I am, for I have voted by myself and privately as others do accessibly,” says Jean Marie Vianney Mukeshimana, who used a Braille voting slate for the first time. “Voting is a deeply emotional and meaningful experience for a person with any disability in Rwanda, reflecting a blend of pride, empowerment, and hope.”

Barriers to the Ballot
Despite legislation like the Americans with Disabilities Act, barriers at the polls still hinder — and often prevent — people with disabilities from voting. New restrictive laws in some states, such as criminalizing assistance with voting, exacerbate these issues. Advocacy groups continue to fight for improved accessibility and increased voter turnout among disabled individuals, emphasizing the need for multiple voting options to accommodate diverse needs. ““Of course, we want to vote,” says Claire Stanley with the American Council of the Blind, “but if you can’t, you can’t.”